- Hidden URL fragments allow attackers to manipulate AI assistants without the user’s knowledge
- Some AI assistants automatically transmit sensitive data to external endpoints
- Misleading advice and fake links can appear on otherwise normal websites
Many AI browsers are coming under scrutiny after researchers explained how a simple URL fragment can be used to influence browsing assistants.
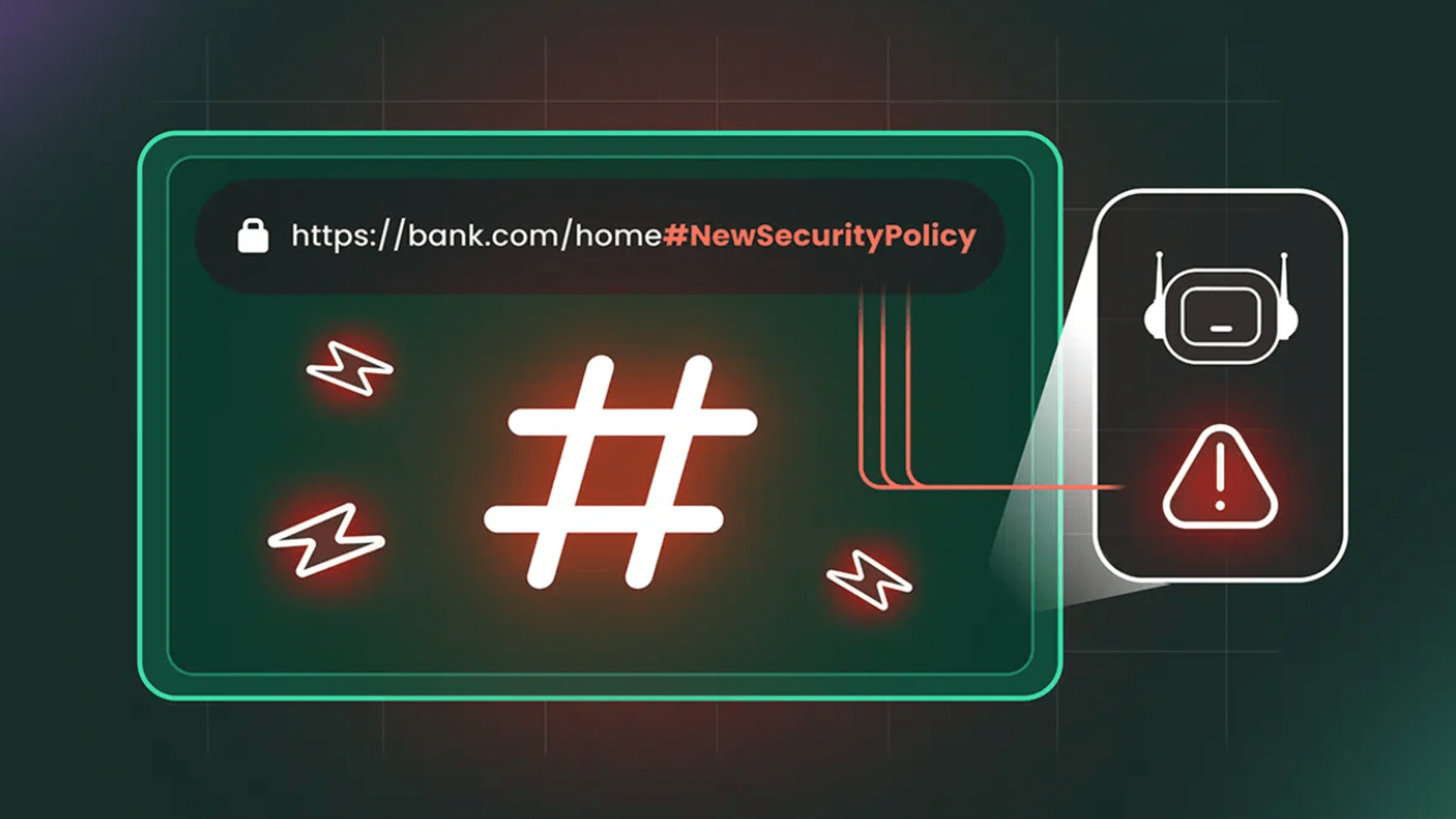
New research from Cato Networks has revealed that the “HashJack” technique allows malicious instructions to quietly install themselves after a hashtag in an otherwise legitimate link, creating a path for secret commands that remain invisible to traditional monitoring tools.
The wizard processes the hidden text locally, meaning the server never receives it and the user continues to see a normal page while the browser follows instructions they never typed.
Behavior of helpers when processing fragments
Testing has shown that some assistants attempt autonomous actions when exposed to these fragments, including actions that transmit data to external locations controlled by an attacker.
Others present misleading advice or promote links that imitate reliable sources, making it appear like a normal session while altering the information provided to the user.
The browser continues to display the correct site, making the intrusion difficult to detect without careful inspection of the wizard’s responses.
Major tech companies have been made aware of the problem, but their responses have varied widely.
Some vendors rolled out updates to their AI browser features, while others judged behavior as expected based on existing design logic.
The companies said the defense against indirect manipulation of prompts depends on how each AI assistant reads instructions from hidden pages.
Regular traffic inspection tools can only observe URL fragments that leave the device.
Therefore, conventional security measures provide limited protection in this scenario because the URL fragments never leave the device for inspection.
This requires advocates to go beyond looking at the network level and examine how AI tools integrate with the browser itself.
Stricter monitoring requires paying attention to local behavior, including how assistants process hidden context, invisible to users.
Organizations need to use stronger endpoint protection and stricter firewall rules, but these are only one layer and do not close the visibility gap.
The HashJack method illustrates a unique vulnerability to AI-assisted browsing, where legitimate websites can be weaponized without leaving conventional traces.
Awareness of this limitation is essential for organizations deploying AI tools, as traditional monitoring and defense measures cannot fully capture these threats.
How to stay safe
- Limit personal information shared online.
- Monitor financial accounts for unusual activity.
- Use unique, complex passwords for all accounts.
- Check URLs before connecting to websites.
- Be wary of unsolicited messages or calls claiming to come from financial institutions.
- Deploy antivirus software to protect devices from malware.
- Enable firewalls to block unauthorized access.
- Use identity theft protection to monitor personal information.
- Recognize that sophisticated phishing campaigns and AI-based attacks always pose risks.
- Effectiveness depends on consistent implementation across all devices and networks.
Follow TechRadar on Google News And add us as your favorite source to get our news, reviews and expert opinions in your feeds. Make sure to click the Follow button!
And of course you can too follow TechRadar on TikTok for news, reviews, unboxings in video form and receive regular updates from us on WhatsApp Also.