The Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela is located along the Caribbean coast of South America. Its neighboring countries are Brazil and Colombia. Having a total area of 912,050 km2 and a surface area of 882,050 km2, Venezuela is rich in natural resources.
Natural resources include oil, natural gas, iron ore, gold, bauxite, diamonds and other minerals.
Oil
The country has one of the largest oil reserves in the world and is a founding member of the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC).
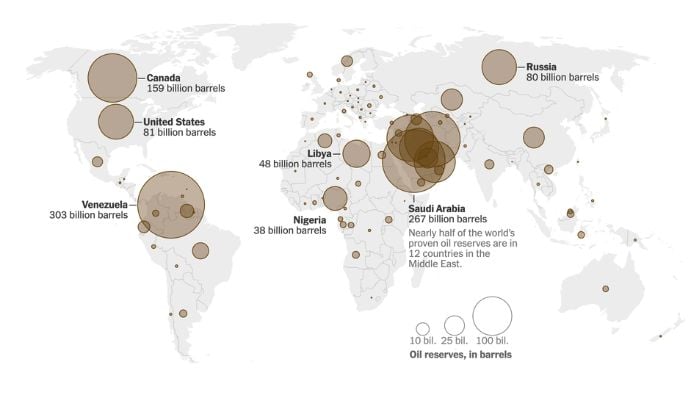
The World Energy Statistical Review found that Venezuela’s proven oil reserves stood at approximately 300 billion barrels (4.8 x 1,010 m3) as of January 1, 2014.
However, the 2019 BP Statistical Review of World Energy reveals that Venezuela’s total proven reserves reached 303.3 billion barrels, slightly more than those of Saudi Arabia (297.7 billion barrels).
In addition to conventional oil reserves, Venezuela has oil sands deposits of similar size to those of Canada in the Orinoco belt. They are roughly equivalent to the world’s reserves of conventional oil.
The Orinoco belt’s recoverable reserves are reported to be between 100 billion and 270 billion barrels. According to the United States Geological Survey (USGS), the Orinoco Belt alone contains between 900 and 1.4 trillion barrels of heavy crude in proven and unproven deposits.
Of this total, only 380 to 652 billion barrels can be technically recoverable. This makes the country’s total reserves (proven and unproven) one of the largest in the world.
Gold
Venezuela has significant gold resources, located mainly in the Guiana Plateau, in the southeast of the country. Gold mining began in the 1800s, and by the early 1970s, approximately 187 metric tons had been officially produced. The El Callao district is the most important gold mining area in Venezuela, having produced more than 124 tons of gold and once being the first gold mine in the world. Other districts, such as Kilometer 88, Lo Increíble and Marwani, also contain gold in similar geological settings.
Diamond
Venezuela is also naturally blessed with diamonds. Its Guiana Plateau is the central diamond-producing region. The Quebrada Grande region and the San Salvador de Paul mine have always been the most important producers, accounting for more than 90% of diamond production between 1975 and 1980.
Iron
Venezuela also has significant iron resources, mainly in the banded iron formations (BIF) of the Archaean Imataca Complex. Currently, high-grade reserves have exceeded 1,866 million metric tons at Cerro Bolivar, San Isidro and Los Barrancos, grading approximately 63% iron. In combination with lower quality materials, total reserves can reach up to 8,000 to 10,000 million metric tons.
Aluminum
After oil, Venezuela’s alumina industry is the second largest source of foreign exchange. In 1987, the country produced approximately 1,347,000 tons of alumina and 428,000 tons of aluminum metal. Important deposits are found at Los Pijiguaos, Upata, Nuria, Los Guaicas and Gran Sabana. Los Pijiguaos alone holds approximately 700 million tonnes of proven and potential reserves.
Manganese
Manganese deposits are present in the greenstone belts of the Archaean Imataca Complex, in locations such as San Cristobal, La Esperanza, El Palmar, Guacuripia, Upata, and El Pao. The ores are then enriched, containing pyrolusite, cryptomelane and psilomelane, with total reserves in the Upata-El Palmar-Guacuripia region of approximately 1 million tonnes, averaging 20-25% Mn.
Tin
Tin occurs in placer, eluvial, and lode deposits in western Bolivar State and the Amazon Federal Territory, particularly around Cano Aguamena. Besides tin, associated minerals include cassiterite, tantalum, niobium, zirconium and titanium. Although the resources are not well defined, drill samples show between 0.01 and 0.77% tin in the heavy minerals.
Niobium, tantalum, rare earth minerals (REE)
These are primarily related to pegmatites of the Parguaza Granite and Imataca Complex, with the richest deposit at Cerro Impacto, an altered carbonatite. The lateritic soils are here enriched in Fe, Mn, Al, Ba, Th, Nb, Ti and REE (Cerium, Lanthanum and Neodymium). Other minerals include gorceixite, goyazite, florencite, bastanaesite and monazite. The most important source is Cerro Impacto.
Uranium
Uranium occurrences are scattered, mainly in the form of radiometric anomalies in the Guiana plateau. Key areas include the Churuata ring structure and parts of the Roraima Group.
Venezuela is blessed with abundant natural resources, including oil, minerals and metals, offering significant economic potential, although many deposits remain underexplored and development varies by region.