- Pezy insists that workloads require more independence than traditional locking execution allows
- SC4 Pezy’s simulations affirm the massive improvements in efficiency in the previous generation conceptions
- Chip made on 5NM TSMC with an unusually large matrix size
At Hot Chips 2025, a small Japanese company known for its unconventional equipment, presented its latest project, the Pey SC4S.
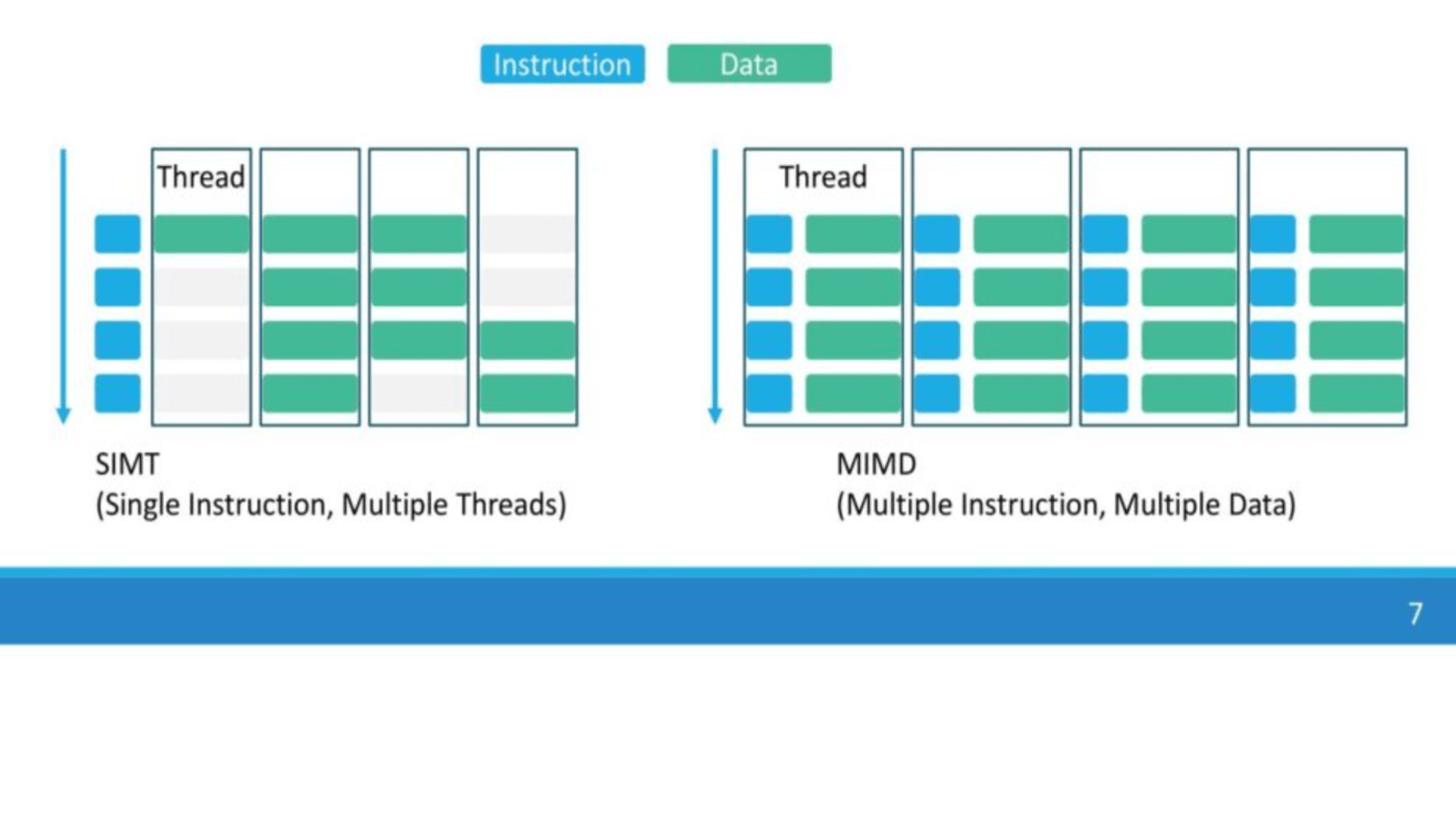
Unlike traditional flea manufacturers who have standardized around the unique education of several data conceptions, Pezy Computing continues to continue several instructions on several data (MIMD).
The MIMD can be compared to a company of state, prefectures, cities and villages, where each unit acts with a degree of independence rather than following a single central authority.
Architecture and choice of manufacturing
MIMD is not a new idea – after all, each modern laptop for programming performs several tasks at the same time, but it has rarely been implemented on a truly massive scale involving hundreds or thousands of hearts.
The design philosophy assumes that future workloads will not always benefit from the execution of locking and that the manipulation of more independent wire could become essential.
This makes its strategy separate from the management of most of the so-called best candidates for the processor who dominate the world market.
SC4S is made on the 5 NM TSMC process and is not a small chip in terms of physical imprint.
With a matrix size of around 556 mm2, it is considerably larger than many consumer or workstation processors.
However, the emphasis is not placed on the minimization of the silicon area but rather on the tests if the advantages of massive parallelism prevail over the costs.
The idea that processors have hundreds of hearts have existed for some time. Pezy maintains that many small semi-autonomous nuclei can succeed when centralized approaches fight.
Indeed, the company bets that IT demand in certain specialized areas justifies this scale, even if such an approach can be impractical for a broader adoption of consumers.
But what Pezy Computing has been published are performance simulations rather than final silicon references, which naturally raises questions about how these affirmations take place in practice.
Compared to its previous SC3 design, the SC4S should offer more than double electrical efficiency when managing a DGEMM workload.
Meanwhile, the simulations of the Smith-Waterman algorithm, used in the alignment of the genome sequence, suggests a quadruple performance increase.
Although these figures are impressive on paper, skepticism remains until the independent tests validate them.
Historically, daring projections in the development of semiconductors are not always aligned with results measured once real material ships.
Although the SC4s are still under development, the company has already paid its attention to a successor.
The work continues on a fifth generation processor, temporarily called Pey 5, which should use a process of 3 nm or more.
A liberation window has been set for 2027, although such long -term calendars in the development of fleas often move due to technical or economic challenges.
Given the scale of the company, industry observers remain cautious about whether the calendar is realistic.
Via serving the house